The goal of this competition is to predict e-commerce clicks, cart additions, and orders. You’ll build a multi-objective recommender system based on previous events in a user session.
这场比赛的目标是预测电子商务点击量、购物车添加量和订单。您将基于用户会话中以前的事件构建一个多目标推荐系统。
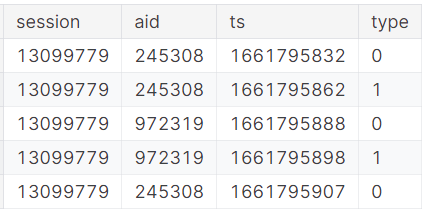
The training data contains full e-commerce session information. For each session in the test data, your task it to predict the aid values for each session type thats occur after the last timestamp ts in the test session. In other words, the test data contains sessions truncated by timestamp, and you are to predict what occurs after the point of truncation.
训练数据包含完整的电子商务会话信息。对于测试数据中的每个会话,您的任务是预测测试会话中最后一个时间戳ts之后出现的每个会话类型的商品编号(20个)。换句话说,测试数据包含按时间戳截断的会话,您要预测截断点之后会发生什么。
总结: 给定每个用户每个时刻的行为(点击,加购,付款)的商品编号,给出下一个时刻,该用户三种行为最可能的20个商品编号.
数据描述:
2,899,779 sessions
训练数据:
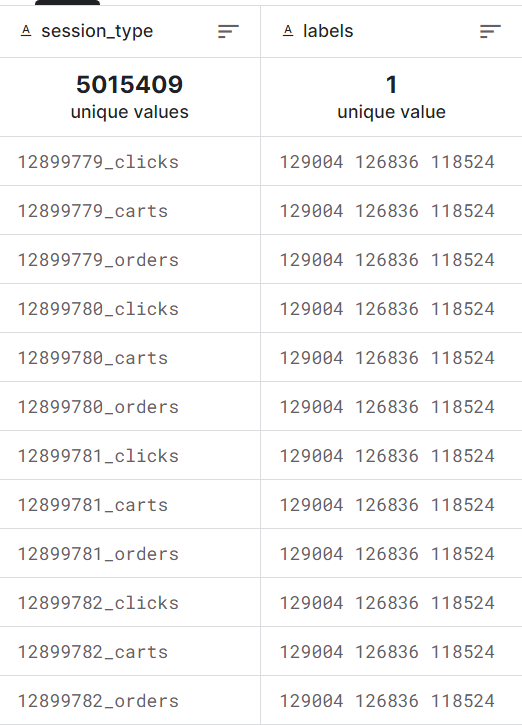
提交样例文件:
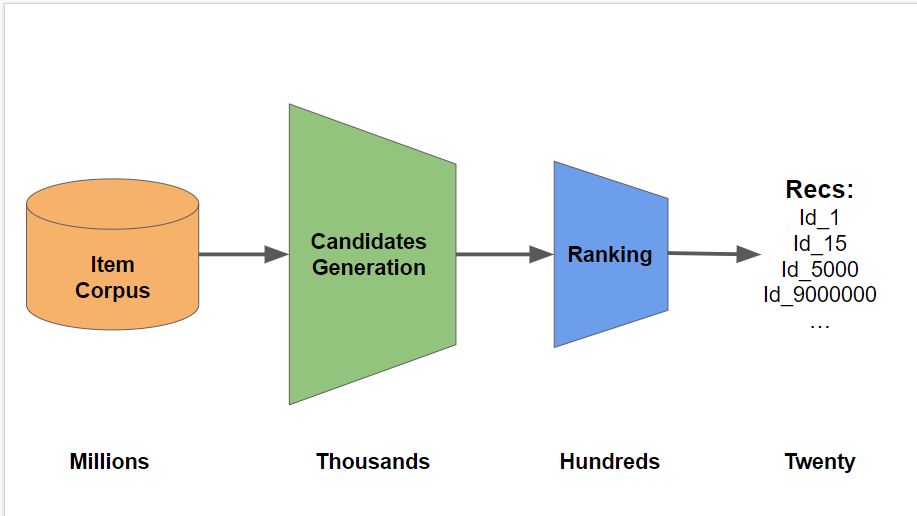
Candidate Generation方法
Step 1 - Generate Candidates
以前购买的物品
回购的物品
总体上最受欢迎的项目
基于某种聚类技术的相似项目
基于共同访问矩阵等类似项目
Step 2 - ReRank and Choose 20
Ranker Model
Handcrafted Rules
What is the co-visitation matrix, really?
It is very interesting to think of modern techniques in the context of their roots.
“Radek is a _”.当我们预测横线上的词的时候, 三元模型会从"Radek", “is”, and “a” 看,然后统计哪个单词和着三个单词出现的次数最多.
但是可能并没有那么多的"Radek", “is”, and "a"的出现过.
那么,这与共访矩阵有什么关系呢?
Candidate ReRank Model - LB 0.575
Step 1 - Generate Candidates
用户点击、购物车、订单的用户历史记录
测试数据一周内最受欢迎的20次点击、购物车、订单
点击/购物车/订单到购物车/订单 的共同访问矩阵(带有类型权重)
称为buy2buy的购物车/订单到购物车/订单的共访问矩阵
点击/购物车/订单与点击的共访问矩阵(带时间权重)
Step 2 - ReRank and Choose 20
最近访问过的项目
以前多次访问的项目
以前在购物车或订单中的项目
购物车/订单到购物车/订单的共同访问矩阵
当前热门项目
“Carts Orders” Co-visitation Matrix - Type Weighted
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 """ 构建思路: 按照用户和时间进行排序 df.groupby('session').cumcount()求出每个用户的行数 保留每个用户最近的30个行为 df.merge(df, on='session')创建每个用户的行为对其他行为的关系(目的是构建商品和商品的关系) 筛选出时间间隔小于1天 且商品编号不相同的行,删除重复的值 根据行为的权重系数,对商品之间的关系进行赋值 得到了每个商品之间的权重系数 """ type_weight = {0 :1 , 1 :6 , 2 :3 } df = df.sort_values(['session' , 'ts' ], ascending=[True , False ]) df = df.reset_index(drop=True ) df['n' ] = df.groupby('session' ).cumcount() df = df.loc[df.n < 30 ].drop('n' , axis=1 ) df = df.merge(df, on='session' ) df = df.loc[((df.ts_x - df.ts_y).abs () < 24 * 60 * 60 ) & (df.aid_x != df.aid_y)] df = df.loc[(df.aid_x >= PART*SIZE) & (df.aid_x < (PART+1 )*SIZE)] df = df[['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'type_y' ]].drop_duplicates(['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]) df['wgt' ] = df.type_y.map (type_weight) df = df[['aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'wgt' ]] df.wgt = df.wgt.astype('float32' ) df = df.groupby(['aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]).wgt.sum ()
“Buy2Buy” Co-visitation Matrix
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 """ 构建思路: 按照用户和时间进行排序 df.groupby('session').cumcount()求出每个用户的行数 保留每个用户最近的30个行为 df.merge(df, on='session')创建每个用户的行为对其他行为的关系(目的是构建商品和商品的关系) 筛选出时间间隔小于14天 且商品编号不相同的行,删除重复的值 权重全部是1(加购和加购之间的关系),对商品和商品之间的关系进行分组求和 得到了每个商品之间的权重系数 """ df = df.loc[df['type' ].isin([1 ,2 ])] df = df.sort_values(['session' ,'ts' ],ascending=[True ,False ]) df = df.reset_index(drop=True ) df['n' ] = df.groupby('session' ).cumcount() df = df.loc[df.n<30 ].drop('n' ,axis=1 ) df = df.merge(df, on='session' ) df = df.loc[((df.ts_x - df.ts_y).abs () < 14 * 24 * 60 * 60 ) & (df.aid_x != df.aid_y)] df = df.loc[(df.aid_x >= PART*SIZE) & (df.aid_x < (PART+1 )*SIZE)] df = df[['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'type_y' ]].drop_duplicates(['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]) df['wgt' ] = 1 df = df[['aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'wgt' ]] df.wgt = df.wgt.astype('float32' ) df = df.groupby(['aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]).wgt.sum ()
“Clicks” Co-visitation Matrix - Time Weighted
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 """ 构建思路: 按照用户和时间进行排序 df.groupby('session').cumcount()求出每个用户的行数 保留每个用户最近的30个行为 df.merge(df, on='session')创建每个用户的行为对其他行为的关系(目的是构建商品和商品的关系) 筛选出时间间隔小于1天 且商品编号不相同的行,删除重复的值 按时间顺序对商品和商品之间的关系进行赋值,时间越近权重越大 得到了每个商品之间的权重系数 """ df = df.sort_values(['session' , 'ts' ], ascending=[True , False ]) df = df.reset_index(drop=True ) df['n' ] = df.groupby('session' ).cumcount() df = df.loc[df.n < 30 ].drop('n' , axis=1 ) df = df.merge(df, on='session' ) df = df.loc[((df.ts_x - df.ts_y).abs () < 24 * 60 * 60 ) & (df.aid_x != df.aid_y)] df = df.loc[(df.aid_x >= PART*SIZE) & (df.aid_x < (PART+1 )*SIZE)] df = df[['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'ts_x' ]].drop_duplicates(['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]) df['wgt' ] = 1 + 3 *(df.ts_x - 1659304800 ) / (1662328791 - 1659304800 ) df = df[['aid_x' , 'aid_y' , 'wgt' ]] df.wgt = df.wgt.astype('float32' ) df = df.groupby(['aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]).wgt.sum ()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 tmp = tmp.reset_index() tmp = tmp.sort_values(['aid_x' ,'wgt' ],ascending=[True ,False ]) tmp = tmp.reset_index(drop=True ) tmp['n' ] = tmp.groupby('aid_x' ).aid_y.cumcount() tmp = tmp.loc[tmp.n<15 ].drop('n' ,axis=1 ) tmp.groupby('aid_x' ).aid_y.apply(list ).to_dict() ''' 总结: 1. "Carts Orders" Co-visitation Matrix - Type Weighted 含义:根据用户的历史行为分配商品之间的权重系数对应top_20_buys 2. "Buy2Buy" Co-visitation Matrix 含义:根据用户的加购和购买行为分配商品之间的权重系数对应top_20_buy2buy 3. "Clicks" Co-visitation Matrix - Time Weighted 含义:根据用户的行为时间分配商品之间的权重系数对应top_20_clicks '''
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 type_weight_multipliers = {0 : 1 , 1 : 6 , 2 : 3 } def suggest_clicks (df ): aids = df.aid.tolist() ty = df.type .tolist() unique_aids = list (dict .fromkeys(aids[::-1 ])) if len (unique_aids) >= 20 : weights = np.logspace(0.1 , 1 , len (aids), base=2 , endpoint=True ) - 1 aids_temp = Counter() for aid, w, t in zip (aids, weights, ty): aids_temp[aid] += w * type_weight_multipliers[t] sorted_aids = [k for k,v in aids_temp.most_common(20 )] return sorted_aids aids2 = list (itertools.chain(*[top_20_clicks[aid] for aid in unique_aids if aid in top_20_click])) top_aids2 = [aid2 for aid2, cnt in Counter(aids2).most_common(20 ) if aid2 not in unique_aids] result = unique_aids + top_aids2[:20 - len (unique_aids)] return result + list (top_clicks)[:20 - len (result)] def suggest_buys (df ): aids = df.aid.tolist() ty = df.type .tolist() unique_aids = list (dict .fromkeys(aids[::-1 ])) df = df.loc[(df['type' ] == 1 ) | (df['type' ] == 2 )] unique_buys = list (dict .fromkeys(df.aid.tolist()[::-1 ])) if len (unique_aids) >= 20 : weights = np.logspace(0.5 , 1 , len (aids), base=2 , endpoint=True ) - 1 aids_temp = Counter() for aid, w, t in zip (aids, weights, types): aids_temp[aid] += w * type_weight_multipliers[t] aids3 = list (itertools.chain(*[top_20_buy2buy[aid] for aid in unique_buys if aid in top_20_buy2buy])) for aid in aids3: aids_temp[aid] += 0.1 sorted_aids = [k for k, v in aids_temp.most_common(20 )] return sorted_aids aids2 = list (itertools.chain(*[top_20_buys[aid] for aid in unique_aids if aid in top_20_buys])) aids3 = list (itertools.chain(*[top_20_buy2buy[aid] for aid in unique_buys if aid in top_20_buy2buy])) top_aids2 = [aid2 for aid2, cnt in Counter(aids2 + aids3).most_common(20 ) if aid2 not in unique_aids] result = unique_aids + top_aids2[:20 - len (unique_aids)] return result + list (top_orders)[:20 - len (result)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 pred_df_clicks = test_df.sort_values(["session" , "ts" ]).groupby(["session" ]).apply( lambda x: suggest_clicks(x) ) pred_df_buys = test_df.sort_values(["session" , "ts" ]).groupby(["session" ]).apply( lambda x: suggest_buys(x) ) clicks_pred_df = pd.DataFrame(pred_df_clicks.add_suffix("_clicks" ), columns=["labels" ]).reset_index() orders_pred_df = pd.DataFrame(pred_df_buys.add_suffix("_orders" ), columns=["labels" ]).reset_index() carts_pred_df = pd.DataFrame(pred_df_buys.add_suffix("_carts" ), columns=["labels" ]).reset_index() pred_df = pd.concat([clicks_pred_df, orders_pred_df, carts_pred_df]) pred_df.columns = ["session_type" , "labels" ] pred_df["labels" ] = pred_df.labels.apply(lambda x: " " .join(map (str ,x))) pred_df.to_csv("submission.csv" , index=False ) pred_df.head()
Co-visitation Matrix
Step 1 - Generate Candidates
总会有一些商品是经常点击的并且一起买,利用这个思想构建一个协同矩阵
首先,我们查看同一会话中在时间上彼此接近(<1天)的所有事件对。我们计算共同访问矩阵M a i d 1 , a i d 2 M_{aid1,aid2} M a i d 1 , a i d 2
对于每个商品id,我们发现前20个最频繁的a i d 2 = a r g s o r t ( M [ a i d ] ) [ − 20 : ] aid2=argsort(M[aid])[-20:] a i d 2 = a r g s o r t ( M [ a i d ] ) [ − 2 0 : ]
Step 2 - ReRank and Choose 20
从上面的候选列表中选择出现频率最高的20个作为最终预测结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import sys import gc def gen_pairs (df ): df = df.query('session % @SAMPLING == 0' ).groupby('session' , as_index=False , sort=False ).apply(lambda g: g.tail(30 )).reset_index(drop=True ) df = pd.merge(df, df, on='session' ) pairs = df.query('abs(ts_x - ts_y) < 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000 and aid_x != aid_y' )[['session' , 'aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]].drop_duplicates() return pairs[['aid_x' , 'aid_y' ]].values def gen_aid_pairs (): all_pairs = defaultdict(lambda : Counter()) all_pair_chunks = [] with tqdm(glob.glob('../input/otto-chunk-data-inparquet-format/*_parquet/*' ), desc='Chunks' ) as prog: for idx, chunk_file in enumerate (prog): with multiprocessing.Pool() as p: chunk = pd.read_parquet(chunk_file).drop(columns=['type' ]) pair_chunks = p.map (gen_pairs, np.array_split(chunk, 120 )) pair_chunks = np.concatenate(pair_chunks, axis=0 ) all_pair_chunks.append(pair_chunks) if DEBUG and idx >= 3 : break del chunk, pair_chunks gc.collect() df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.concatenate(all_pair_chunks), columns=['aid1' , 'aid2' ]) top_aids = df.groupby('aid1' ).apply(lambda df: Counter(df.aid2).most_common(40 )).to_dict() return top_aids
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import itertoolsdef suggest_aids (df ): aids = df.tail(20 ).aid.tolist() if len (aids) >= 20 : return aids aids = set (aids) new_aids = Counter() for aid in aids: new_aids.update(top_40_cnt.get(aid, Counter())) top_aids2 = [aid2 for aid2, cnt in new_aids.most_common(20 ) if aid2 not in aids] return list (aids) + top_aids2[:20 - len (aids)] pred_df = test_df.sort_values(["session" , "type" , "ts" ]).groupby(["session" ]).apply( lambda x: suggest_aids(x) )
🏆 Training an XGBoost Ranker on the GPU 🔥🔥🔥 💡 [polars] Proof of concept: LGBM Ranker🧪🧪🧪 How To Build a GBT Ranker Model
Step 1 - Generate Candidates
session (i.e. user)
aid (i.e. item)
user features
item features
user-item interaction features
click target (i.e 0 or 1)
cart target (i.e. 0 or 1)
order target (i.e. 0 or 1)
Step 2 - ReRank and Choose 20
Step 1
session
aid
1
1234
1
9841
2
5845
2
8984
Setp 2
1 2 3 item_features = train.groupby('aid' ).agg({'aid' :'count' ,'session' :'nunique' ,'type' :'mean' }) item_features.columns = ['item_item_count' ,'item_user_count' ,'item_buy_ratio' ]
Setp 3
1 2 3 user_features = train.groupby('session' ).agg({'session' :'count' ,'aid' :'nunique' ,'type' :'mean' }) user_features.columns = ['user_user_count' ,'user_item_count' ,'user_buy_ratio' ]
Setp 4
Setp 5
1 2 candidates = candidates.merge(item_features, left_on='aid' , right_index=True , how='left' ).fillna(-1 ) candidates = candidates.merge(user_features, left_on='session' , right_index=True , how='left' ).fillna(-1 )
然后candidate dataframe类似:
session
aid
item_feat1
item_feat2
user_feat1
user_feat2
1
1234
1
2
3
4
1
9841
5
6
7
8
2
5845
9
10
11
12
2
8984
13
14
15
16
Setp 6test_labels.parquet😐 session | type | ground_truth |
然后将其转换为如下:
session
aid
cart
1
5456
1
1
4545
1
1
98741
1
然后将其合并到candidate dataframe中
1 candidates = candidates.merge(cart_target,on=['user' ,'item' ],how='left' ).fillna(0 )
candidates dataframe类似:
session
aid
item_feat1
item_feat2
user_feat1
user_feat2
cart
1
1234
1
2
3
4
0
1
9841
5
6
7
8
1
2
5845
9
10
11
12
0
2
8984
13
14
15
16
1
Setp 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import xgboost as xgb from sklearn.model_selection import GroupKFold skf = GroupKFold(n_splits=5 ) for fold, (train_idx, valid_idx) in enumerate (skf.split(candidates, candidates['click' ], groups=candidates['user' ])): X_train = candidates.loc[train_idx, FEATURES] y_train = candidates.loc[train_idx, 'click' ] X_valid = candidates.loc[valid_idx, FEATURES] y_valid = candidates.loc[valid_idx, 'click' ] dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train, group=[50 ] * (len (train_idx)//50 ) ) dvalid = xgb.DMatrix(X_valid, y_valid, group=[50 ] * (len (valid_idx)//50 ) ) xgb_parms = {'objective' :'rank:pairwise' , 'tree_method' :'gpu_hist' } model = xgb.train(xgb_parms, dtrain=dtrain, evals=[(dtrain,'train' ),(dvalid,'valid' )], num_boost_round=1000 , verbose_eval=100 ) model.save_model(f'XGB_fold{fold} _click.xgb' )
Setp 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 preds = np.zeros(len (test_candidates)) for fold in range (5 ): model = xgb.Booster() model.load_model(f'XGB_fold{fold} _click.xgb' ) model.set_param({'predictor' : 'gpu_predictor' }) dtest = xgb.DMatrix(data=test_candidates[FEATURES]) preds += model.predict(dtest)/5 predictions = test_candidates[['user' ,'item' ]].copy() predictions['pred' ] = preds predictions = predictions.sort_values(['user' ,'pred' ], ascending=[True ,False ]).reset_index(drop=True ) predictions['n' ] = predictions.groupby('user' ).item.cumcount().astype('int8' ) predictions = predictions.loc[predictions.n<20 ] sub = predictions.groupby('user' ).item.apply(list ) sub = sub.to_frame().reset_index() sub.item = sub.item.apply(lambda x: " " .join(map (str ,x))) sub.columns = ['session_type' ,'labels' ] sub.session_type = sub.session_type.astype('str' )+ '_clicks'
💡 Word2Vec How-to [training and submission]🚀🚀🚀
A session where one action follows another action is very much like a sentence!
类似地,在这里我们可以利用这样一个事实,即在一个紧密的序列中出现的商品id可能有一些相似之处。
所以我们使用word2vec模型来训练商品id的嵌入向量,然后使用这些向量来计算商品id之间的相似度。
这样给定一个商品的id就可以找到和她类似的商品id。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 sentences_df = pl.concat([train, test]).groupby('session' ).agg( pl.col('aid' ).alias('sentence' ) ) sentences = sentences_df['sentence' ].to_list() w2vec = Word2Vec(sentences=sentences, vector_size=32 , min_count=1 , workers=4 ) aid2idx = {aid: i for i, aid in enumerate (w2vec. index_to_key)} index = AnnoyIndex(32 , 'euclidean' ) for aid, idx in aid2idx.items(): index.add_item(idx, w2vec.wv.vectors[idx]) index.build(10 ) sample_sub = pd.read_csv('../input/otto-recommender-system//sample_submission.csv' ) ''' 选择最近的20个商品 ''' test_session_AIDs = test.to_pandas().reset_index(drop=True ).groupby('session' )['aid' ].apply(list ) test_session_types = test.to_pandas().reset_index(drop=True ).groupby('session' )['type' ].apply(list ) labels = [] type_weight_multipliers = {0 : 1 , 1 : 6 , 2 : 3 } for AIDs, types in zip (test_session_AIDs, test_session_types): if len (AIDs) >= 20 : weights=np.logspace(0.1 ,1 ,len (AIDs),base=2 , endpoint=True )-1 aids_temp=defaultdict(lambda : 0 ) for aid,w,t in zip (AIDs,weights,types): aids_temp[aid]+= w * type_weight_multipliers[t] sorted_aids=[k for k, v in sorted (aids_temp.items(), key=lambda item: -item[1 ])] labels.append(sorted_aids[:20 ]) else : AIDs = list (dict .fromkeys(AIDs[::-1 ])) most_recent_aid = AIDs[0 ] nns = [w2vec.wv.index_to_key[i] for i in index.get_nns_by_item(aid2idx[most_recent_aid], 21 )[1 :]] labels.append((AIDs+nns)[:20 ])
和covisiation matrix类似,使用word2vec可以获取最相关的商品
数据为:
session
aid
type
1
10
0
1
20
0
2
20
1
2
30
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 假如通过上面的代码我们已经类似的获取到了最相关的商品 | session | aid | | --- | --- | | 1 | 11 | | 1 | 20 | | 2 | 25 | | 2 | 6 | 那么下面还有几个步骤 1. Step 1 : Add ordering information to our candidates.word2vec模型是按照相似度评分来排序的,所以我们需要添加一些排序信息 | session | aid | rank | | --- | --- | --- | | 1 | 11 | 1 | | 1 | 20 | 2 | | 2 | 25 | 1 | | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2. 将这些信息合并到candidates中| session | aid | rank | type | | --- | --- | --- | --- | | 1 | 11 | 1 | null | | 1 | 20 | 2 | 0 | | 1 | 10 | null | 0 | | 2 | 25 | 1 | null | | 2 | 6 | 2 | null | | 2 | 20 | null | 1 | | 2 | 30 | null | 0 | 3. 使用Ranker模型进行预测,[💡 [2 methods] How-to ensemble predictions 🏅🏅🏅](https://www.kaggle.com/code/radek1/2 -methods-how-to-ensemble-predictions) 对预测结果集成: - 投票集成(voting ensemble) - 加权投票集成(voting ensemble with weights),对好结果有更大的权重 ```python def read_sub (path, weight=1 ): '''a helper function for loading and preprocessing submissions''' return ( pl.read_csv(path) .with_column(pl.col('labels' ).str .split(by=' ' )) .with_column(pl.lit(weight).alias('vote' )) .explode('labels' ) .rename({'labels' : 'aid' }) .with_column(pl.col('aid' ).cast(pl.UInt32)) .with_column(pl.col('vote' ).cast(pl.UInt8)) ) subs = [read_sub(path) for path in paths] subs = [read_sub(path, weight) for path, weight in zip (paths, [1 , 0.55 , 0.55 ])]
读取后的数据为:
session_type
aid
vote
1_clicks
1234
1
1_clicks
9841
1
2_clicks
5845
1
由于内存限制,只能进行join:
1 2 subs = subs[0 ].join(subs[1 ], how='outer' , on=['session_type' , 'aid' ]).join(subs[2 ], how='outer' , on=['session_type' , 'aid' ], suffix='_right2' ) subs.head()
合并后的数据
session_type
aid
vote
vote_right
vote_right2
1_clicks
1234
1
1
1
1_clicks
9841
1
null
1
2_clicks
5845
1
1
null
2_clicks
8984
1
null
null
用0填充null值,然后对vote求和,排序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 subs = (subs .fill_null(0 ) .with_column((pl.col('vote' ) + pl.col('vote_right' ) + pl.col('vote_right2' )).alias('vote_sum' )) .drop(['vote' , 'vote_right' , 'vote_right2' ]) .sort(by='vote_sum' ) .reverse() )
数据如下:
session_type
aid
vote_sum
1_clicks
1234
3
2_clicks
5845
2
1_clicks
9841
2
然后对每个类型选择前20个商品,然后聚合成数组:
1 2 3 4 5 preds = subs.groupby('session_type' ).agg([ pl.col('aid' ).head(20 ).alias('labels' ) ]) preds = preds.with_column(pl.col('labels' ).apply(lambda lst: ' ' .join([str (aid) for aid in lst])))
与word2vec类似,使用矩阵分解来获取商品的嵌入向量
💡Matrix Factorization with GPU [PyTorch+Merlin Dataloader]
使用Pytorch的Embedding层来训练商品的嵌入向量,然后使用这些向量来计算商品id之间的相似度.
1 2 3 4 5 6 train_pairs = cudf.concat([train, test])[['session' , 'aid' ]] del train, testtrain_pairs['aid_next' ] = train_pairs.groupby('session' ).aid.shift(-1 ) train_pairs = train_pairs[['aid' , 'aid_next' ]].dropna().reset_index(drop=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import torchfrom torch import nnclass MatrixFactorization (nn.Module): def __init__ (self, n_aids, n_factors ): super ().__init__() self.aid_factors = nn.Embedding(n_aids, n_factors, sparse=True ) def forward (self, aid1, aid2 ): aid1 = self.aid_factors(aid1) aid2 = self.aid_factors(aid2) return (aid1 * aid2).sum (dim=1 ) class AverageMeter (object ): """Computes and stores the average and current value""" def __init__ (self, name, fmt=':f' ): self.name = name self.fmt = fmt self.reset() def reset (self ): self.val = 0 self.avg = 0 self.sum = 0 self.count = 0 def update (self, val, n=1 ): self.val = val self.sum += val * n self.count += n self.avg = self.sum / self.count def __str__ (self ): fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})' return fmtstr.format (**self.__dict__)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 model.to('cuda' ) for epoch in range (num_epochs): for batch, _ in train_dl_merlin: model.train() losses = AverageMeter('Loss' , ':.4e' ) aid1, aid2 = batch['aid' ], batch['aid_next' ] aid1 = aid1.to('cuda' ) aid2 = aid2.to('cuda' ) output_pos = model(aid1, aid2) output_neg = model(aid1, aid2[torch.randperm(aid2.shape[0 ])]) output = torch.cat([output_pos, output_neg]) targets = torch.cat([torch.ones_like(output_pos), torch.zeros_like(output_pos)]) loss = criterion(output, targets) losses.update(loss.item()) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() model.eval () with torch.no_grad(): accuracy = AverageMeter('accuracy' ) for batch, _ in valid_dl_merlin: aid1, aid2 = batch['aid' ], batch['aid_next' ] output_pos = model(aid1, aid2) output_neg = model(aid1, aid2[torch.randperm(aid2.shape[0 ])]) accuracy_batch = torch.cat([output_pos.sigmoid() > 0.5 , output_neg.sigmoid() < 0.5 ]).float ().mean() accuracy.update(accuracy_batch, aid1.shape[0 ]) print (f'{epoch+1 :02d} : * TrainLoss {losses.avg:.3 f} * Accuracy {accuracy.avg:.3 f} ' )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 embeddings = model.aid_factors.weight.detach().cpu().numpy() knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors=21 , metric='euclidean' ) knn.fit(embeddings) _, aid_nns = knn.kneighbors(embeddings) sample_sub = pd.read_csv('../input/otto-recommender-system//sample_submission.csv' ) test = cudf.read_parquet('../input/otto-full-optimized-memory-footprint/test.parquet' ) session_types = ['clicks' , 'carts' , 'orders' ] gr = test.reset_index(drop=True ).to_pandas().groupby('session' ) test_session_AIDs = gr['aid' ].apply(list ) test_session_types = gr['type' ].apply(list ) labels = [] type_weight_multipliers = {0 : 1 , 1 : 6 , 2 : 3 } for AIDs, types in zip (test_session_AIDs, test_session_types): if len (AIDs) >= 20 : weights=np.logspace(0.1 ,1 ,len (AIDs),base=2 , endpoint=True )-1 aids_temp=defaultdict(lambda : 0 ) for aid,w,t in zip (AIDs,weights,types): aids_temp[aid]+= w * type_weight_multipliers[t] sorted_aids=[k for k, v in sorted (aids_temp.items(), key=lambda item: -item[1 ])] labels.append(sorted_aids[:20 ]) else : AIDs = list (dict .fromkeys(AIDs[::-1 ])) most_recent_aid = AIDs[0 ] nns = list (aid_nns[most_recent_aid]) labels.append((AIDs+nns)[:20 ]) labels_as_strings = [' ' .join([str (l) for l in lls]) for lls in labels] predictions = pd.DataFrame(data={'session_type' : test_session_AIDs.index, 'labels' : labels_as_strings}) prediction_dfs = [] for st in session_types: modified_predictions = predictions.copy() modified_predictions.session_type = modified_predictions.session_type.astype('str' ) + f'_{st} ' prediction_dfs.append(modified_predictions) submission = pd.concat(prediction_dfs).reset_index(drop=True ) submission.to_csv('submission.csv' , index=False )
226th (?!) Place Solution & Two-cents from a First-timer
Item Co-visitation Matrix
Order matrix: Click/cart/order to click/cart/order with type weighting
Buy2buy matrix: Cart/order to cart/order
Click matrix: click/cart/order to clicks with time weighting
Feature Feneration
Item features (for each aid)
Count of events (click/cart/order)
Quarter of day (QoD) with most events (0-3)
Day of week (DoW) with most events (0-6)
User features (for each session)
Count of events (click/cart/order) and interacted items (aid)
QoD with most events (0-3)
DoW with most events (0-6)
Number of days with events
Days from first to last events
User-item features (for each session-aid pair)
Count of events (click/cart/order) and interacted items (aid)
QoD with most events in both categorical (0-3) and one-hot encoded (0/1 for each) format
DoW with most events in both categorical (0-6) and one-hot encoded (0/1 for each) format
last_n = item_chronological_rank / user_total_event_count
last_ts = (user_item_last_timestamp - start_week_timestamp) / (end_week_timestamp - start_week_timestamp)
Candidate Selection
会话单击/点选/订购项目的次数
共访权总和
该商品是否为本周点击次数最多/购买次数最多的商品
Ranker
Rule-base ranker in Chris’ notebook
XGBRanker with rank:pairwise objective
the model is overfitting and requires a lot of hyperparameter tuning
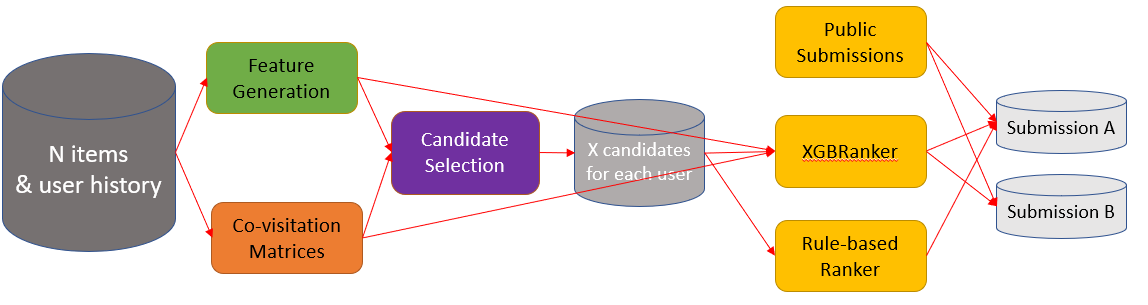
Solution Ensemble
use their public LB scores as weights
Ensemble of XGBRanker above and public submissions
Ensemble of above two ranker methods and public submissions
6, what have I learned
read the discussion and notebooks forums
try as many ideas as possible
know every line of code you write